Is your 5G deployment underway?
Optimize Your Network Infrastructure
The increased bandwidth and faster speeds promised by 5G connectivity will enable applications such as high-definition video, ultra-low-latency gaming and advanced telemedicine. As operators race to deploy their 5G networks, availability and security are paramount, but managing the inevitable spike in energy consumption is a looming challenge.
There are steps operators can take to reduce the energy their networks consume, source energy wisely, and ensure more responsible operation. We can help. We are Vertiv.
Read the White PaperUnderstand What’s Happening in the Network
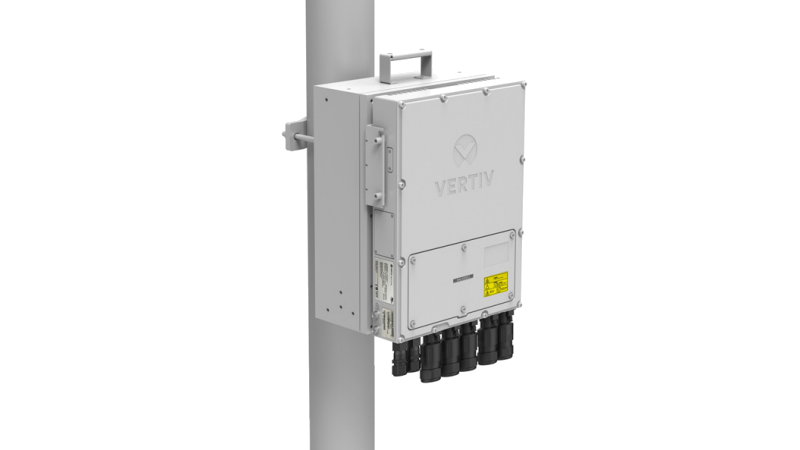
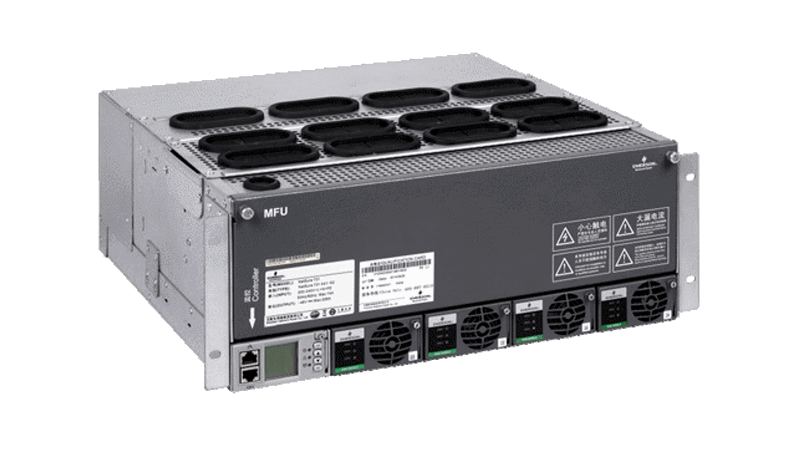
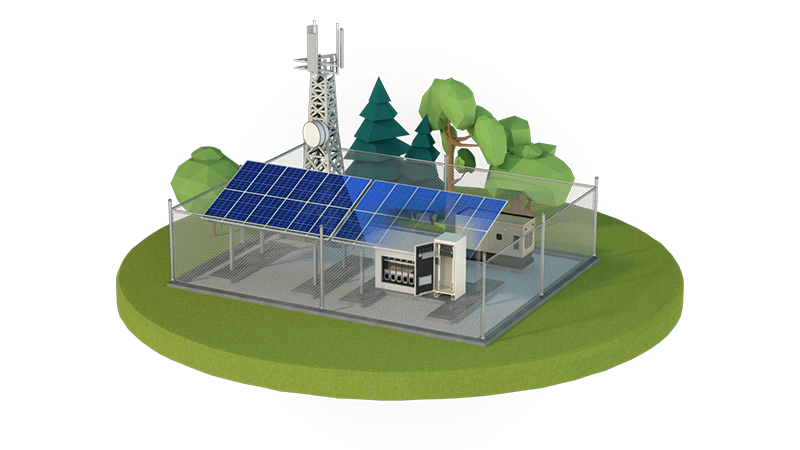
Place Vertiv™ NetSure™ IPE outdoor rectifiers next to radio equipment at the top of poles, towers, or buildings to reduce voltage drop.
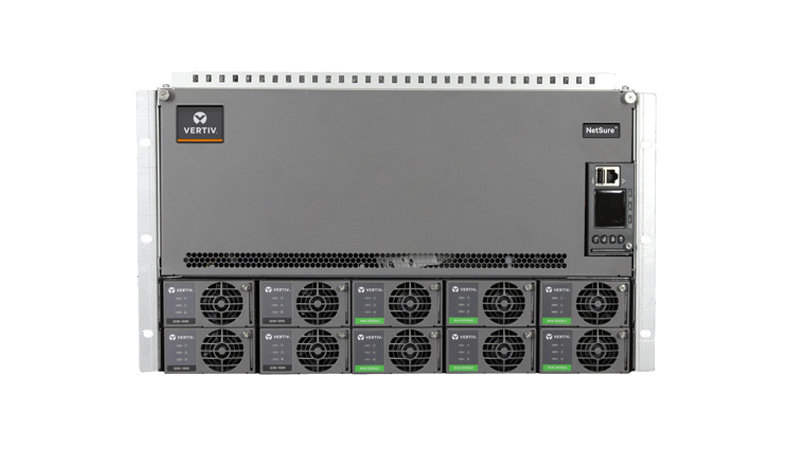
Vertiv™ NetSure™ Inverter systems with market leading power density backup your edge equipment using a single battery bank for AC and DC systems. Plus, they can be field added to an existing system on site.
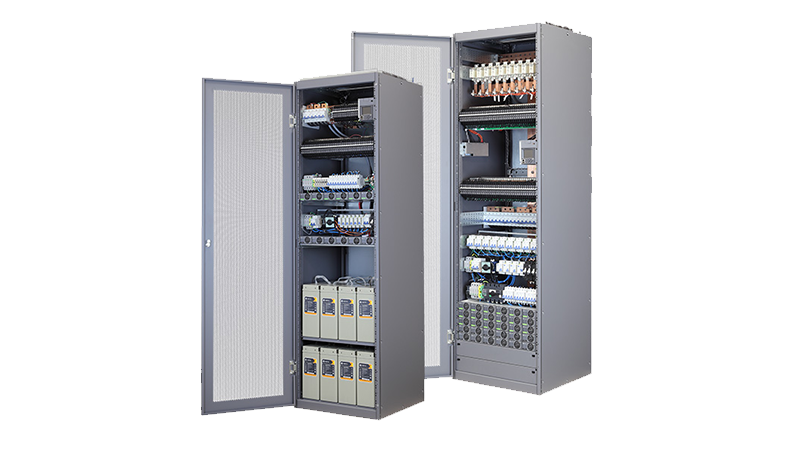
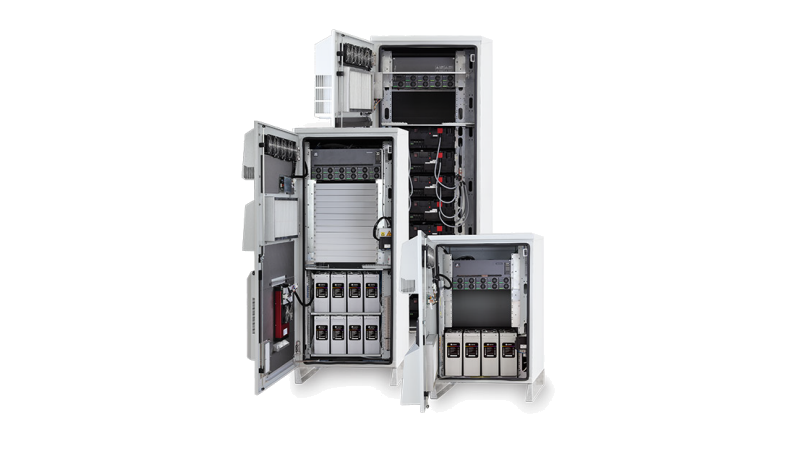
Standardize on a single prefabricated form factor with Vertiv™ NetSure™ outdoor enclosures to dramatically reduce pre-planning and installation time cycle.
Learn about ways to reduce energy consumption in the telecom access network. Download the white paper.
Featured Success Stories

Alternative Energy to Offer Connectivity in the Paraguayan Chaco
February 24, 2022An important telecommunications company with a regional presence requested a special project to provide, install and commission solar power stations to provide connectivity in the area of the Pilcomayo River deep in the Paraguayan Chaco.
Read MoreLatest Research

Vertiv Guide to 5G Technology
Vertiv has created an in-depth Guide to 5G Technology where you can learn more about core facilities, edge networks and the 5G infrastructure needed across the access landscape. Discover the latest 5G research from Vertiv including, industry reports, videos, blog articles and more.